Cross Applications
- Cross Application
- Cross Applications is the concept to exchange data between two systems.
- ALE (Application Link Enabling) is an SAP Technology to support Cross Applications.
- ALE uses IDOC(Intermediate Documents) to support the cross applications
- IDOC is the carrier to carry the data from one system to another system.
- SAP can only understand the IDOC format when it communicates with any other system.
- Irrespective of the Receivers, the ABAPer’s job in the sender system is to generate the IDOC. The Process of Generating the IDOC is nothing but an Outbound Process.
- Irrespective of the senders, The ABAPer’s job in the receiver system is to collect the data from IDOC. The process is collecting the data from IDOC is nothing but Inbound Process.
Run Time Components of IDOC's
Run Time Components of IDOC:
- It generates and unique IDOC Number, Which is 16 digits.
- It generates 3 types of records.
- Control Record
- Data Records
- Status Records
Control Records: Control records specify the sender as well as receiver information. It generates only one control record. This information will be saved on EDIDC Table.
Data Records: Data records specify the data which is sent by the sender system. It generates any number of data records. This information will be saved on EDIDD Table.
Status Records: It generates the status code for each and every stage of transferring the data. It generates any number of status records. This information will be saved on the EDIDS table. There are 2 types of status codes.
- Outbound Status code ( 0-49)
- Inbound Status Code (50-75)
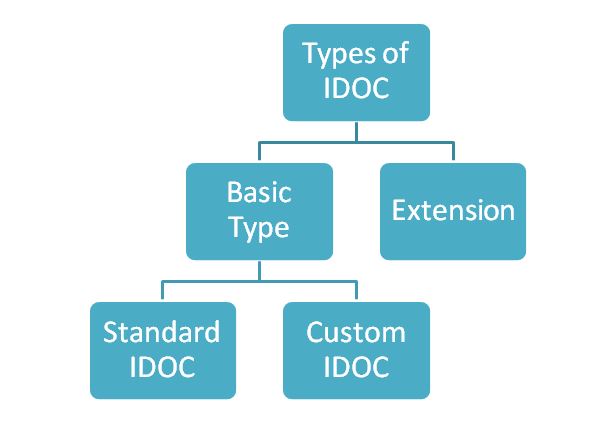
Types of IDOC
Types of IDOC:
- Basic Types:
- Standard IDOC
- Custom IDOC
- Extension
Standard IDOC: if we want to send as well as receive the standard database table information then we go for the standard IDC eg. LFA1 table.
Custom IDOC: If we want to send as well as receive the custom table information then we go for custom IDOC
E.g.
|
Employee ID |
|
Employee Name |
|
Employee Contact number |
Extension IDOC: If we want to send as well as receive additional fields information of the standard database table along with standard fields information then we go for extension IDOC.
E.g.
|
Employee ID |
|
Employee Name |
|
Employee Contact number |
|
KNA1 |
|
LIFNR |
|
KUNNR |
Structure of an IDOC:
IDOC is the collection of segments and each segment is the collection of fields.
WE31 is the transaction code to create the segment.
WE30 is the transaction code to create the IDOC as well as display the IDOC.
Characteristics of an IDOC
IDOC Outbound Process
IDOC Inbound Process
IDOC Filtering Techniques
IDOC Change Pointer Techniques
Custom IDOC
Extended IDOC
ALE uses IDOC ( Intermediate Documents) to support the Cross-Application.
IDOC is the carrier that carries the data from one system to another system. SAP only understands the IDOC format while communicating with other systems.
Runtime Components of IDOC
It generates a 16 digit Unique IDOC number.
It generates three types of records control Record
Data Record
Status Record
Control Record
Control Record
It specifies the sender and receiver information
It generates only one record
This information will be saved on EDIDC Table
Data Record
It specifies the data which is sent by the sender system.
It generates any number of Data Records
This information will be saved on EDIDD Table
Status Record
It generates the status record of every stage of transferring the data.
It generates any number of status records.
This information will be saved on EDIDS Table.
There are 2 types of Status records.
Inbound Status code ( 50 – 75)
Outbound Status code ( 0-49)
Types of IDOC
| Standard IDOC | Custom IDOC | Extension IDOC |
| If we want to send as well as receive the standard database table information then we will go for standard IDOC | IF we want to send and receive the custom table information then we will go for custom IDOC. | If we want to send and receive additional field information then we go for Extension IDOC. |
